Like countless others, I frittered away the better part of Jan. 6 doomscrolling and watching television coverage of the horrifying events unfolding in our nation’s capital, where a mob of President Trump supporters and QAnon conspiracy theorists was incited to lay siege to the U.S. Capitol. For those trying to draw meaning from the experience, might I suggest consulting the literary classic Moby Dick, which simultaneously holds clues about QAnon’s origins and offers an apt allegory about a modern-day Captain Ahab and his ill-fated obsessions.
Many have speculated that Jim Watkins, the administrator of the online message board 8chan (a.k.a. 8kun), and/or his son Ron are in fact “Q,” the anonymous persona behind the QAnon conspiracy theory, which holds that President Trump is secretly working to save the world from a satanic cult of pedophiles and cannibals.
Last year, as I was scrutinizing the computer networks that kept QAnon online, researcher Ron Guilmette pointed out a tantalizing utterance from Watkins the younger which adds tenuous credence to the notion that one or both of them is Q.

We’ll get to how the Great White Whale (the Capitol?) fits into this tale in a moment. But first, a bit of background. A person identified only as “Q” has for years built an impressive following for the far-right conspiracy movement by leaving periodic “Q drops,” cryptic messages that QAnon adherents spend much time and effort trying to decipher and relate to current events.
Researchers who have studied more than 5,000 Q drops are convinced that there are two distinct authors of these coded utterances. The leading theory is that those identities corresponded to the aforementioned father-and-son team responsible for operating 8chan.
Jim Watkins, 56, is the current owner of 8chan, a community perhaps now best known as a forum for violent extremists and mass shooters. Watkins is an American pig farmer based in the Philippines; Ron reportedly resides in Japan.
In the aftermath of back-to-back mass shootings on Aug. 3 and Aug. 4, 2019 in which a manifesto justifying one of the attacks was uploaded to 8chan, Cloudflare stopped providing their content delivery network to 8chan. Several other providers quickly followed suit, leaving 8chan offline for months before it found a haven at a notorious bulletproof hosting facility in Russia.
One reason Q watchers believe Ron and Jim Watkins may share authorship over the Q drops is that while 8chan was offline, the messages from Q ceased. The drops reappeared only months later when 8chan rebranded as 8kun.
CALL ME ISHMAEL
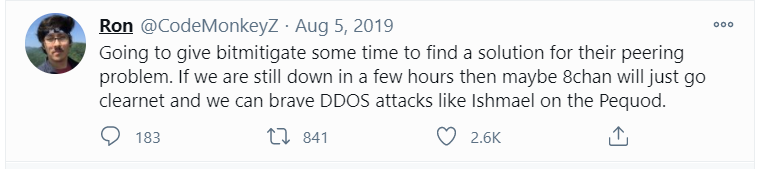
Here’s where the admittedly “Qonspiratorial” clue about the Watkins’ connection to Q comes in. On Aug. 5, 2019, Ron Watkins posted a Twitter message about 8chan’s ostracization which compared the community’s fate to that of the Pequod, the name of the doomed whaling ship in the Herman Melville classic “Moby Dick.”
“If we are still down in a few hours then maybe 8chan will just go clearnet and we can brave DDOS attacks like Ishmael on the Pequod,” Watkins the younger wrote.
Ishmael, the first-person narrator in the novel, is a somewhat disaffected American sailor who decides to try his hand at a whaling ship. Ishmael is a bit of a minor character in the book; very soon into the novel we are introduced to a much more interesting and enigmatic figure — a Polynesian harpooner by the name of Queequeg.
Apart from being a cannibal from the Pacific islands who has devoured many people, Queequeg is a pretty nice guy and shows Ismael the ropes of whaling life. Queequeg is covered head to toe in tattoos, which are described by the narrator as the work of a departed prophet and seer from the cannibal’s home island.
 Like so many Q drops, Queequeg’s tattoos tell a mysterious tale, but we never quite learn what that full story is. Indeed, the artist who etched them into Queequeg’s body is long dead, and the cannibal himself can’t seem to explain what it all means.
Like so many Q drops, Queequeg’s tattoos tell a mysterious tale, but we never quite learn what that full story is. Indeed, the artist who etched them into Queequeg’s body is long dead, and the cannibal himself can’t seem to explain what it all means.
Ishmael describes Queequeg’s mysterious markings in this passage:
“…a complete theory of the heavens and earth, and a mystical treatise on the art of attaining truth; so that Queequeg in his own proper person was a riddle to unfold; a wondrous work in one volume; but whose mysteries not even himself could read, though his own live heart beat against them; and these mysteries were therefore destined in the end to moulder away with the living parchment whereon they were inscribed, and so be unsolved to the last.”
THE GREAT WHITE WHALE
It’s perhaps fitting then that one of the most recognizable figures from the mob that stormed the U.S. Capitol on Wednesday was a heavily-tattooed, spear-wielding QAnon leader who goes by the name “Q Shaman” (a.k.a. Jake Angeli).
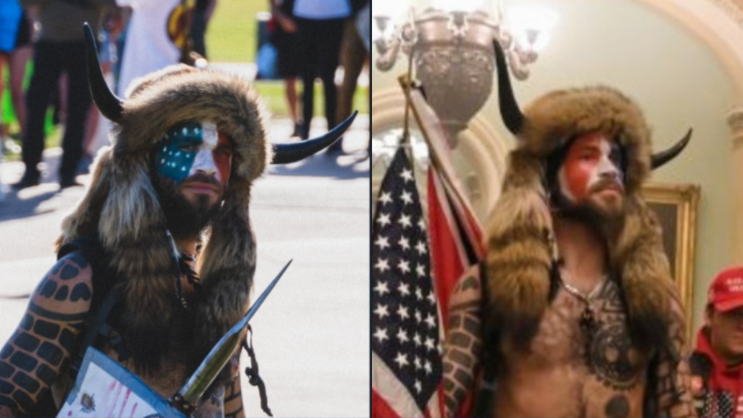

“Q Shaman,” a.k.a. Jake Angeli, at a Black Lives Matter event in Arizona (left) and Wednesday, confronted by U.S. Capitol Police. Image: Twitter, @KelemenCari.
“Angeli’s presence at the riot, along with others wearing QAnon paraphernalia, comes as the conspiracy-theory movement has been responsible for the popularization of Trump’s voter-fraud conspiracy theories,” writes Rachel E. Greenspan for Yahoo! News.
“As Q has become increasingly hands-off, giving fewer and fewer messages to his devotees, QAnon leaders like Angeli have gained fame and power in the movement,” Greenspan wrote.
If somehow Moby Dick was indeed the inspiration for the “Q” identity in QAnon, yesterday’s events at The Capitol were the inexorable denouement of a presidential term that increasingly came to be defined by conspiracy theories. In a somewhat prescient Hartford Courant op-ed published in 2018, author Steven Almond observed that Trump’s presidency could be best understood through the lens of the Pequod’s Captain Ahab. To wit:
“Melville is offering a mythic account of how one man’s virile bombast ensnares everyone and everything it encounters. The setting is nautical, the language epic. But the tale, stripped to its ribs, is about the seductive power of the wounded male ego, how naturally a ship steered by men might tack to its vengeful course.”
“Trump’s presidency has been, in its way, a retelling of this epic. Whether we cast him as agent or principal hardly matters. What matters is that Americans have joined the quest. In rapture or disgust, we’ve turned away from the compass of self-governance and toward the mesmerizing drama of aggression on display, the masculine id unchained and all that it unchains within us. With every vitriolic tweet storm and demeaning comment, Trump strikes through the mask.”
EPILOGUE
If all of the above theorizing reads like yet another crackpot QAnon conspiracy, that may be the inevitable consequence of my spending far too much time going down this particular rabbit hole (and re-reading Moby Dick in the process!).
In any case, none of this is likely to matter to the diehard QAnon conspiracy theorists themselves, says Mike Rothschild, a writer who specializes in researching and debunking conspiracy theories.
“Even if Jim Watkins was revealed as owning the board or making the posts, it wouldn’t matter,” Rothschild said. “Anything that happens that disconfirms Q being an official in the military industrial complex is going to help fuel their persecution complex.”
Rothschild has been working hard on finishing his next book, “The Storm is Upon Us: How QAnon Became a Movement, Cult, and Conspiracy Theory of Everything,” which is due to be published in October 2021. Who’s printing the book? Ten points if you guessed Melville House, an independent publisher named after Herman Melville.
from Krebs on Security https://ift.tt/393XphW
via IFTTT




 Like so many Q drops, Queequeg’s tattoos tell a mysterious tale, but we never quite learn what that full story is. Indeed, the artist who etched them into Queequeg’s body is long dead, and the cannibal himself can’t seem to explain what it all means.
Like so many Q drops, Queequeg’s tattoos tell a mysterious tale, but we never quite learn what that full story is. Indeed, the artist who etched them into Queequeg’s body is long dead, and the cannibal himself can’t seem to explain what it all means.
 Hace poco se dio a conocer la liberación de una versión correctiva del navegador web Chrome 87.0.4280.141, versión que llega a solucionar 16 vulnerabilidades de las cuales 12 problemas están marcados como peligrosos.
Hace poco se dio a conocer la liberación de una versión correctiva del navegador web Chrome 87.0.4280.141, versión que llega a solucionar 16 vulnerabilidades de las cuales 12 problemas están marcados como peligrosos.