Happy February! Welcome the leap month with these snazzy deals on tech and games.
from Gear Latest https://ift.tt/fP23Bz4
via IFTTT

Happy February! Welcome the leap month with these snazzy deals on tech and games.
from Gear Latest https://ift.tt/fP23Bz4
via IFTTT

By Tripp Mickle
The iPhone maker’s share price dropped in after-hour trading even though sales and profit topped Wall Street expectations.
Published: February 1, 2024 at 04:05PM
from NYT Technology https://ift.tt/zkZHCRy
via IFTTT

By Mike Isaac
The company’s quarterly revenue rose 25% as its costs fell after layoffs last year.
Published: February 1, 2024 at 03:21PM
from NYT Technology https://ift.tt/905KTeA
via IFTTT

By Mike Isaac
The company’s quarterly revenue rose 25% as its costs fell after layoffs last year.
Published: February 1, 2024 at 03:21PM
from NYT Technology https://ift.tt/3cxM1z8
via IFTTT

By Karen Weise
The tech giant introduced the Rufus chatbot. It has lagged behind others on introducing consumer-facing generative artificial intelligence.
Published: February 1, 2024 at 03:04PM
from NYT Technology https://ift.tt/V3Q7GD1
via IFTTT

ReiserFS es un sistema de archivos de propósito general
Hace poco Frederick Brennan compartió una de las cartas que recibió por parte de Hans Reiser, el creador del sistema de archivos ReiserFS, en la cual habló sobre la obsolescencia de ReiserFS V3 en el kernel de Linux.
En las cartas publicadas, Hans lamenta sus errores al interactuar con la comunidad de desarrolladores, analiza la obsolescencia de ReiserFS v3 en el kernel de Linux 6.6, analiza la historia del desarrollo de ReiserFS, menciona las esperanzas asociadas con la promoción de ReiserFS v4 y explica algunas soluciones técnicas implementadas en ReiserFS v4.
Para quienes desconocen de Hans Reiser, deben saber que este es el creador del sistema de archivos ReiserFS y quien en 2008 fue condenado a cadena perpetua por el asesinato de su esposa como resultado de una pelea con un posterior intento de encubrir el crimen. (En 2027, Hans podrá presentar una solicitud de libertad condicional).
Saludos LKML.
Lo que sigue es una carta de Hans Reiser dirigida a mí, que escribió hace unos dos meses y me pidió que la publicara, con sus pensamientos sobre la desaprobación de ReiserFS del kernel de Linux. Lo he transcrito lo mejor que he podido.
Hans Reiser compartió sus puntos de vista sobre la eliminación de ReiserFS V3 del kernel de Linux en la siguiente carta a bordar la decisión de eliminar ReiserFS del kernel, Hans destaca que la utilidad continua de este sistema de archivos y su inclusión en el kernel deberían ser decididas por los usuarios y mantenedores, teniendo en cuenta las realidades actuales.
Ademas de ello, reconoce que mantener el código de ReiserFS en el kernel supone una carga adicional para los mantenedores, quienes deben probar y garantizar la compatibilidad con las nuevas características del kernel. Si ReiserFS ya no es relevante, no tiene sentido mantenerlo como parte del Kernel. Aunque durante el desarrollo de ReiserFS v4 se abordaron muchas deficiencias de la versión 3 y se simplificó el mantenimiento, esta versión nunca fue aceptada en el kernel.
Hans hace una solicitud única: agregar un archivo README que acompañe al código de ReiserFS antes de su eliminación del kernel. En este README, menciona a Mikhail Gilulu, Konstantin Shvachko y Anatoly Pinchuk, cuyas contribuciones al desarrollo fueron subestimadas.
Estos desarrolladores fueron contratados por Hans y contribuyeron al desarrollo de ReiserFS. Sin embargo, debido al carácter exigente de Hans y a sus expectativas poco realistas (trabajaba las veinticuatro horas del día y esperaba el mismo nivel de entusiasmo de los demás), abandonaron el proyecto. Aunque inicialmente Hans percibió esto como una traición, con el tiempo comprendió que su decisión estaba justificada dadas las circunstancias.
Y es que en la carta se menciona que el desarrollo de Reiser v4 no estuvo exento de dificultades y desafíos personales. Hans Reiser reflexiona sobre su experiencia y reconoce los errores cometidos a lo largo del camino. Desde la falta de comunicación efectiva hasta la resistencia al cambio, Hans Reiser comparte las lecciones aprendidas y las áreas en las que podría haber actuado de manera diferente.
Una de las lecciones más importantes que Hans Reiser destaca es la importancia de la colaboración y la comunicación en el desarrollo de software. Reconoce la necesidad de superar la hostilidad inicial y cultivar relaciones positivas con la comunidad de desarrollo.
A pesar de los desafíos y las controversias, el legado de Reiser v4 perdura como un testimonio del poder de la innovación y la determinación. Su arquitectura modular y su enfoque en la eficiencia y la flexibilidad continúan siendo fuentes de inspiración para los desarrolladores de sistemas de archivos.
Finalmente, si estás interesado en poder conocer más al respecto, puedes consultar los detalles de la carta en el siguiente enlace.
from Linux Adictos https://ift.tt/ncfObr9
via IFTTT
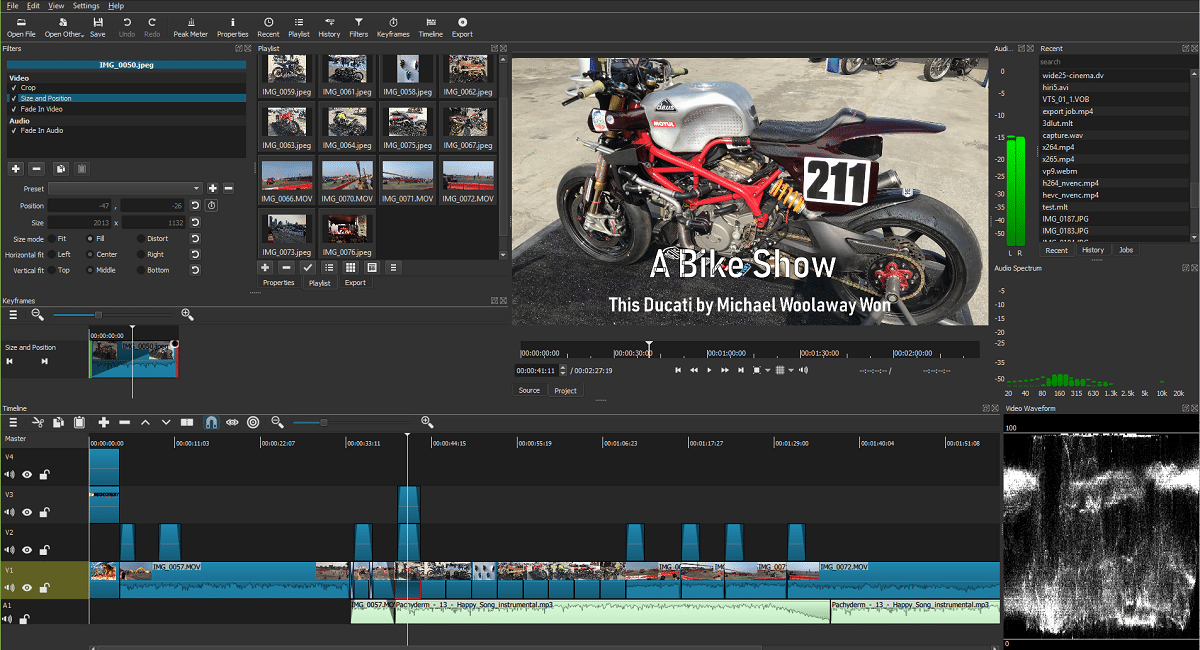
Shotcut: un editor de video gratuito, de código abierto y multiplataforma
Se dio a conocer el lanzamiento de la nueva versión de Shotcut 24.01 y entre las novedades más destacadas se encuentra la implementación de una API de audio SDL_AUDIODRIVER en Linux y Windows, nuevas opciones de copia de seguridad, soporte para múltiples selecciones en la función «Split At Playhead», correcciones de errores y más.
Para quienes desconocen de Shotcut, deben saber que es un software de edición de vídeo que implementa el soporte para formatos de vídeo y audio a través de FFmpeg. Puede utilizar complementos con la implementación de efectos de vídeo y audio que sean compatibles con Frei0r y LADSPA.
En esta nueva versión de Shotcut 24.01 se destaca la implementación de la API de audio en el menú «Configuración> Reproductor» para que la opcion «–SDL_AUDIODRIVER» de línea de comando esté disponible en el menú, para seleccionar el controlador de salida de audio en Linux y Windows .
Además de ello, también se destaca que se agregaron los botones «Loop» y «Set Loop Range» al menú «Player» para controlar el bucle de reproducción, asi como también un botón al cuadro de diálogo de visualización de registros para ir al último registro de sesión (shotcut-log.bak) y un botón para copiar contenido al portapapeles a todos los cuadros de diálogo que muestran texto (similar a las operaciones «Seleccionar todo» y «Copiar» en el menú contextual).
En esta nueva versión de Shotcut 24.01 también se añade un submenú «Archivo > Otras versiones» para identificar otras versiones de proyectos con nombres similares creados por el sistema de respaldo, asi como también la capacidad de agrupar áreas seleccionadas en la línea de tiempo (Línea de tiempo > Selección > Agrupar/Desagrupar).
Otro de los aspectos destacados de este lanzamiento, es que ahora es posible realizar selección múltiple en la función Split At Playhead, además de que se añadió un nuevo modo de división de pistas «Línea de tiempo > Editar > Dividir todas las pistas en el cabezal de reproducción» y la capacidad de realizar operaciones en múltiples elementos seleccionados en «Línea de tiempo > Selección > Agrupar/Desagrupar (Ctrl+G, Command+G en macOS)«.
De los demás cambios que se destacan:
Finalmente si estás interesado en conocer más al respecto sobre esta nueva versión, puedes consultar los detalles en el siguiente enlace.
Para los que son usuarios de Ubuntu y sus derivados, pueden instalar esta aplicación añadiendo el repositorio de la aplicación a su sistema. Para ello debemos de abrir una terminal con Ctrl + Alt + T y en ella vamos a ejecutar lo siguiente.
Primero vamos a añadir el repositorio con:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:haraldhv/shotcut
Luego actualizamos el listado de paquetes y repositorios con este comando:
sudo apt-get update
Finalmente procedemos a instalar la aplicación con:
sudo apt-get install shotcut
Y listo con ello se habrá instalado en el sistema.
Para el resto de las distribuciones de Linux contamos con 3 métodos generales para poder obtener resta aplicación.
La primera de ellas es mediante el uso de Flatpak, por lo que deben de tener el soporte para este tipo de aplicaciones a su sistema.
Después deben de abrir una terminal y en ella teclear el siguiente comando:
flatpak install flathub org.shotcut.Shotcut
Y listo con ello ya instalaron esta aplicación.
Otro método con el que contamos para poder obtener este editor es descargando la aplicación en su formato AppImage, el cual nos da la facilidad de poder utilizar esta aplicación sin necesidad de instalar o añadir cosas al sistema.
Para ello basta con abrir una y en ella ejecutar el siguiente comando:
wget https://github.com/mltframework/shotcut/releases/download/v24.01.28/shotcut-linux-x86_64-240128.AppImage -O shotcut.appimage
Hecho esto ahora debemos de darle permisos de ejecución al archivo descargado con:
sudo chmod +x shotcut.appimage
Y finalmente podemos ejecutar la aplicación con el siguiente comando:
./shotcut.appimage
El ultimo método es con ayuda de los paquetes Snap y para instalar la aplicación debemos de ejecutar el siguiente comando:
sudo snap install shotcut --classic
from Linux Adictos https://ift.tt/HS29Rma
via IFTTT
Three Americans were charged this week with stealing more than $400 million in a November 2022 SIM-swapping attack. The U.S. government did not name the victim organization, but there is every indication that the money was stolen from the now-defunct cryptocurrency exchange FTX, which had just filed for bankruptcy on that same day.
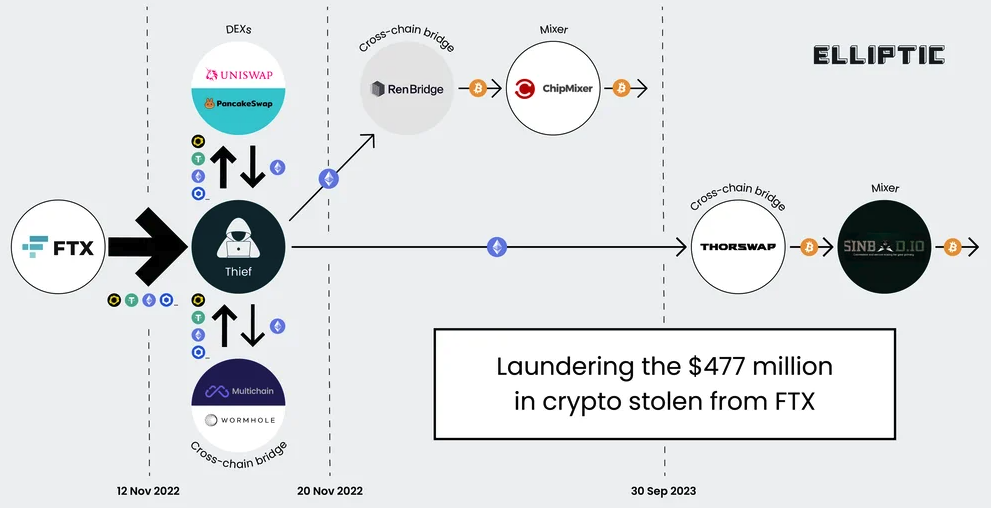
A graphic illustrating the flow of more than $400 million in cryptocurrencies stolen from FTX on Nov. 11-12, 2022. Image: Elliptic.co.
An indictment unsealed this week and first reported on by Ars Technica alleges that Chicago man Robert Powell, a.k.a. “R,” “R$” and “ElSwapo1,” was the ringleader of a SIM-swapping group called the “Powell SIM Swapping Crew.” Colorado resident Emily “Em” Hernandez allegedly helped the group gain access to victim devices in service of SIM-swapping attacks between March 2021 and April 2023. Indiana resident Carter Rohn, a.k.a. “Carti,” and “Punslayer,” allegedly assisted in compromising devices.
In a SIM-swapping attack, the crooks transfer the target’s phone number to a device they control, allowing them to intercept any text messages or phone calls sent to the victim, including one-time passcodes for authentication or password reset links sent via SMS.
The indictment states that the perpetrators in this heist stole the $400 million in cryptocurrencies on Nov. 11, 2022 after they SIM-swapped an AT&T customer by impersonating them at a retail store using a fake ID. However, the document refers to the victim in this case only by the name “Victim 1.”
Wired’s Andy Greenberg recently wrote about FTX’s all-night race to stop a $1 billion crypto heist that occurred on the evening of November 11:
“FTX’s staff had already endured one of the worst days in the company’s short life. What had recently been one of the world’s top cryptocurrency exchanges, valued at $32 billion only 10 months earlier, had just declared bankruptcy. Executives had, after an extended struggle, persuaded the company’s CEO, Sam Bankman-Fried, to hand over the reins to John Ray III, a new chief executive now tasked with shepherding the company through a nightmarish thicket of debts, many of which it seemed to have no means to pay.”
“FTX had, it seemed, hit rock bottom. Until someone—a thief or thieves who have yet to be identified—chose that particular moment to make things far worse. That Friday evening, exhausted FTX staffers began to see mysterious outflows of the company’s cryptocurrency, publicly captured on the Etherscan website that tracks the Ethereum blockchain, representing hundreds of millions of dollars worth of crypto being stolen in real time.”
The indictment says the $400 million was stolen over several hours between November 11 and 12, 2022. Tom Robinson, co-founder of the blockchain intelligence firm Elliptic, said the attackers in the FTX heist began to drain FTX wallets on the evening of Nov. 11, 2022 local time, and continuing until the 12th of November.
Robinson said Elliptic is not aware of any other crypto heists of that magnitude occurring on that date.
“We put the value of the cryptoassets stolen at $477 million,” Robinson said. “The FTX administrators have reported overall losses due to “unauthorized third-party transfers” of $413 million – the discrepancy is likely due to subsequent seizure and return of some of the stolen assets. Either way, it’s certainly over $400 million, and we are not aware of any other thefts from crypto exchanges on this scale, on this date.”
The SIM-swappers allegedly responsible for the $400 million crypto theft are all U.S. residents. But there are some indications they had help from organized cybercriminals based in Russia. In October 2023, Elliptic released a report that found the money stolen from FTX had been laundered through exchanges with ties to criminal groups based in Russia.
“A Russia-linked actor seems a stronger possibility,” Elliptic wrote. “Of the stolen assets that can be traced through ChipMixer, significant amounts are combined with funds from Russia-linked criminal groups, including ransomware gangs and darknet markets, before being sent to exchanges. This points to the involvement of a broker or other intermediary with a nexus in Russia.”
Nick Bax, director of analytics at the cryptocurrency wallet recovery firm Unciphered, said the flow of stolen FTX funds looks more like what his team has seen from groups based in Eastern Europe and Russian than anything they’ve witnessed from US-based SIM-swappers.
“I was a bit surprised by this development but it seems to be consistent with reports from CISA [the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency] and others that “Scattered Spider” has worked with [ransomware] groups like ALPHV/BlackCat,” Bax said.
CISA’s alert on Scattered Spider says they are a cybercriminal group that targets large companies and their contracted information technology (IT) help desks.
“Scattered Spider threat actors, per trusted third parties, have typically engaged in data theft for extortion and have also been known to utilize BlackCat/ALPHV ransomware alongside their usual TTPs,” CISA said, referring to the group’s signature “Tactics, Techniques an Procedures.”
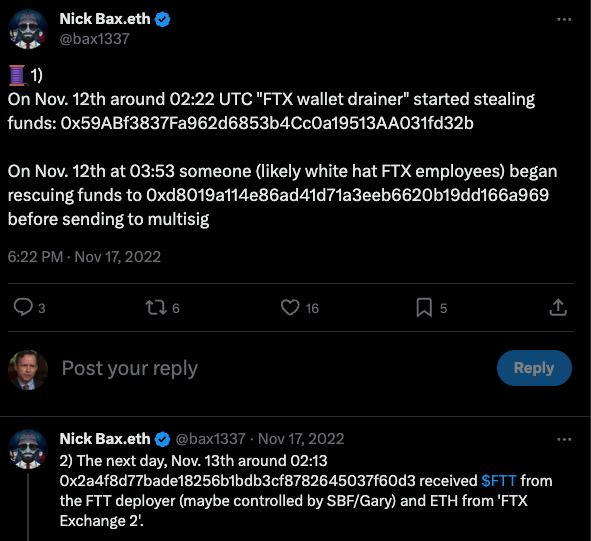
Nick Bax, posting on Twitter/X in Nov 2022 about his research on the $400 million FTX heist.
Earlier this week, KrebsOnSecurity published a story noting that a Florida man recently charged with being part of a SIM-swapping conspiracy is thought to be a key member of Scattered Spider, a hacking group also known as 0ktapus. That group has been blamed for a string of cyber intrusions at major U.S. technology companies during the summer of 2022.
Financial claims involving FTX’s bankruptcy proceedings are being handled by the financial and risk consulting giant Kroll. In August 2023, Kroll suffered its own breach after a Kroll employee was SIM-swapped. According to Kroll, the thieves stole user information for multiple cryptocurrency platforms that rely on Kroll services to handle bankruptcy proceedings.
KrebsOnSecurity sought comment for this story from Kroll, the FBI, the prosecuting attorneys, and Sullivan & Cromwell, the law firm handling the FTX bankruptcy. This story will be updated in the event any of them respond.
Attorneys for Mr. Powell said they do not know who Victim 1 is in the indictment, as the government hasn’t shared that information yet. Powell’s next court date is a detention hearing on Feb. 2, 2024.
from Krebs on Security https://ift.tt/YjLB4Uz
via IFTTT
There are too many great features turned off by default. Rectify that with these tips.
from Gear Latest https://ift.tt/e5TkKwU
via IFTTT

By Kashmir Hill
Readers who have taken the plunge said it had improved their lives, marriages and mental health, and offered advice to those going without their smartphones for “Flip Phone February.”
Published: February 1, 2024 at 12:06PM
from NYT Technology https://ift.tt/giI5EFP
via IFTTT