“Aoqin Dragon” has been operating since at least 2013, with targets including government and telecommunications companies in multiple countries.
from Dark Reading https://ift.tt/lnSjbt2
via IFTTT

“Aoqin Dragon” has been operating since at least 2013, with targets including government and telecommunications companies in multiple countries.
from Dark Reading https://ift.tt/lnSjbt2
via IFTTT
Cybercrime groups that specialize in stealing corporate data and demanding a ransom not to publish it have tried countless approaches to shaming their victims into paying. The latest innovation in ratcheting up the heat comes from the ALPHV/BlackCat ransomware group, which has traditionally published any stolen victim data on the Dark Web. Today, however, the group began publishing individual victim websites on the public Internet, with the leaked data made available in an easily searchable form.
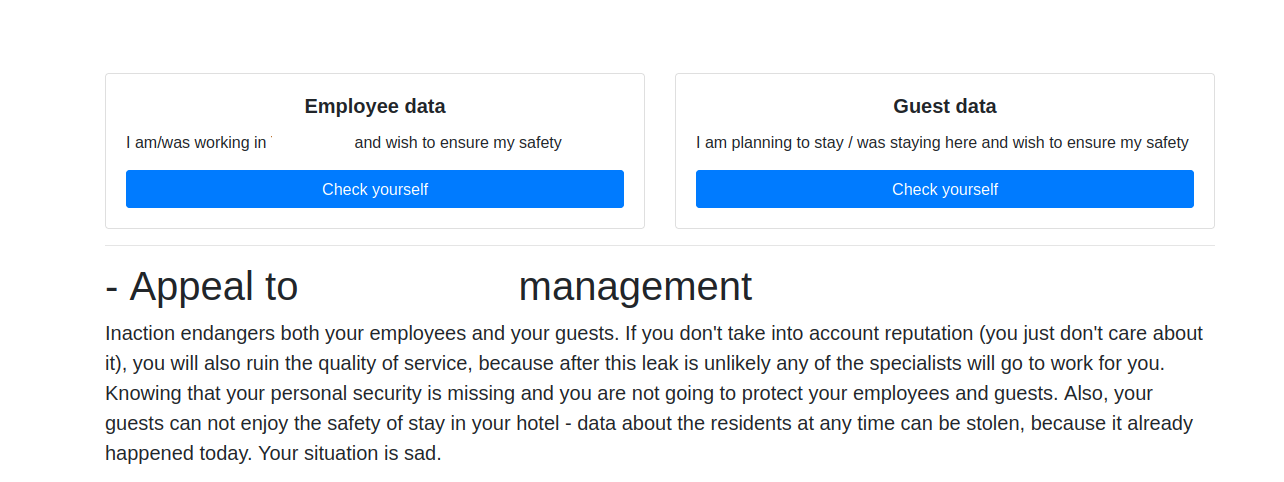
The ALPHV site claims to care about people’s privacy, but they let anyone view the sensitive stolen data.
ALPHV recently announced on its victim shaming and extortion website that it had hacked a luxury spa and resort in the western United States. Sometime in the last 24 hours, ALPHV published a website with the same victim’s name in the domain, and their logo on the homepage.
The website claims to list the personal information of 1,500 resort employees, and more than 2,500 residents at the facility. At the top of the page are two “Check Yourself” buttons, one for employees, and another for guests.
Brett Callow, a threat analyst with security firm Emsisoft, called the move by ALPHV “a cunning tactic” that will most certainly worry their other victims.
Callow said most of the victim shaming blogs maintained by the major ransomware and data ransom groups exist on obscure, slow-loading sites on the Darknet, reachable only through the use of third-party software like Tor. But the website erected by ALPHV as part of this new pressure tactic is available on the open Internet.
“Companies will likely be more concerned about the prospect of their data being shared in this way than of simply being posted to an obscure Tor site for which barely anyone knows the URL,” Callow said. “It’ll piss people off and make class actions more likely.”
It’s unclear if ALPHV plans to pursue this approach with every victim, but other recent victims of the crime group include a school district and a U.S. city. Most likely, this is a test run to see if it improves results.
“We are not going to stop, our leak distribution department will do their best to bury your business,” the victim website reads. “At this point, you still have a chance to keep your hotel’s security and reputation. We strongly advise you to be proactive in your negotiations; you do not have much time.”
Emerging in November 2021, ALPHV is perhaps most notable for its programming language (it is written in Rust). ALPHV has been actively recruiting operators from several ransomware organizations — including REvil, BlackMatter and DarkSide — offering affiliates up to 90 percent of any ransom paid by a victim organization.
Many security experts believe ALPHV/BlackCat is simply a rebrand of another ransomware group — “Darkside” a.k.a. “BlackMatter,” the same gang responsible for the 2021 attack on Colonial Pipeline that caused fuel shortages and price spikes for several days last summer.
Callow said there may be an upside to this ALPHV innovation, noting that his wife recently heard directly from a different ransomware group — Cl0p.
“On a positive note, stunts like this mean people may actually find out that their PI has been compromised,” he said. “Cl0p emailed my wife last year. The company that lost her data still hasn’t made any public disclosure or notified the people who were impacted (at least, she hasn’t heard from the company.)”
from Krebs on Security https://ift.tt/gfrNQKa
via IFTTT
Health gains at the IX Summit of the Americas
Cristina Mitchell
14 Jun 2022
from PAHO/WHO | Pan American Health Organization https://ift.tt/KAlRz20
via IFTTT
Mobile apps that rely on facial recognition for identity proofing can now detect fraudulent attempts to fake liveness.
from Dark Reading https://ift.tt/uvjCOfP
via IFTTT
SBOMs should be connected with vulnerability databases to fulfill their promise of reducing risk, Google security team says.
from Dark Reading https://ift.tt/OiIPaeA
via IFTTT

By BY SHIRA OVIDE
The market for tech talent, and for workers of all types at tech companies, remains hot.
Published: June 14, 2022 at 12:26PM
from NYT Technology https://ift.tt/QVarAbH
via IFTTT
“Aoqin Dragon” has been operating since at least 2013, with targets including government and telecommunications companies in multiple countries.
from Dark Reading https://ift.tt/lnSjbt2
via IFTTT
Martyn Ryder from Morphean explains why forging trusted partnerships is integral to the future of physical security in a world of networks, systems, and the cloud.
from Dark Reading https://ift.tt/41a53Yx
via IFTTT
O! What a tangled web we weave, when first we practise to deceive.
from Naked Security https://ift.tt/sX2xSjr
via IFTTT
New open source database details the software that cloud service providers typically silently install on enterprises’ virtual machines — often unbeknownst to customers.
from Dark Reading https://ift.tt/lczaYRO
via IFTTT