
By BY DON CLARK
The deal, which was initially valued at $40 billion, encountered regulatory scrutiny, including an F.T.C. lawsuit.
Published: February 7, 2022 at 08:26PM
from NYT Technology https://ift.tt/FPyjmCH
via IFTTT


By BY DON CLARK
The deal, which was initially valued at $40 billion, encountered regulatory scrutiny, including an F.T.C. lawsuit.
Published: February 7, 2022 at 08:26PM
from NYT Technology https://ift.tt/FPyjmCH
via IFTTT
Actinium/Gameredon’s attacks are another reminder of why organizations need to pay additional scrutiny to systems in the region.
from Dark Reading https://ift.tt/s5LQNPV
via IFTTT

(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
Agosto fue un mes relativamente tranquilo para el año bastante movido en materia de tecnología. Continúa la pérdida de usuarios de Firefox, Google demuestra que la privacidad no es algo que se le dé muy bien y, dos festejos de cumpleaños
Aclaro una vez más que no estoy en una campaña en contra de Firefox. Los directivos de la Fundación Mozilla no necesitan de mi ayuda para destruir al otrora orgullo del código abierto.
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
Mientras la Fundación Mozilla dedica todos sus esfuerzos a la corrección política, el navegador de código abierto y única alternativa a Google Chrome perdió unos 50 millones de dólares por año. Eso sería unos 46 000 usuarios por día.
Gran parte de esa estadística pertenece a dispositivos móviles que traen integrados sus propios navegadores. Google Chrome en Android y Safari en iOS. Edge, en Windows mejoró notablemente sus prestaciones y, es mucho más probable que aquellos a los que no les guste instalen Chrome.
También, la integración de Chrome con los servicios de Google y con Edge y los servicios de Microsoft es mucho mejor que con Firefox. Y, por supuesto no podemos negar la influencia de la incesante publicidad de Google en su buscador.
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
Pero, eso no significa que neguemos los propios errores de Mozilla; el despido de empleados valiosos, el abandono de proyectos o la pérdida de tiempo en cosas que no tienen nada que ver con el desarrollo de software.
Este fue un año de cuestionamiento a las grandes tecnológicas y uno de los temas es la forma en la que protegen los datos de los usuarios. Ya comentamos la forma en que Apple aceptó compartir con el gobierno chino los datos de los usuarios de iCloud, llegando a ceder la operación a una empresa estatal china dentro de sus fronteras.
En el caso de Google se supo que entre 2019 y 2021 despidió a 80 empleados por prácticas como el robo y posterior filtración de información interna de la empresa y el acceso no autorizado a datos de usuarios.
De todas formas, un portavoz de la empresa restó importancia al tema:
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
Las instancias a las que se hace referencia se relacionan principalmente con el acceso inapropiado o el uso indebido de información corporativa o IP privada y confidencial».
«La cantidad de infracciones, ya sean deliberadas o inadvertidas, es constantemente baja. Todos los empleados reciben capacitación anualmente, investigamos todas las acusaciones y las infracciones dan lugar a medidas correctivas que incluyen el despido y contamos con procesos estrictos para proteger los datos de los clientes y usuarios de cualquier amenaza interna o externa
En agosto se celebraron dos cumpleaños muy relevantes para todos nosotros.
Un 31 de agosto de 1991, cierto estudiante finlandés anunció que estaba desarrollando un nuevo sistema operativo, para lo cual había portado dos herramientas del proyecto GNU; bash y gcc. Una quincena después se producía el lanzamiento de la primera versión del kernel.
Ese primer kernel ocupaba 62 KB en forma comprimida y contenía alrededor de 10 mil líneas de código fuente. Las versiones actuales cuentan con más de 20 millones de líneas de código
24 días antes del anuncio de Linus Torvalds, el científico británico Tim Berners-Lee público el primer sitio web,
La dirección del primer sitio web fue «https://ift.tt/7qOcuPb, y llevaba a una página que contenía enlaces a información sobre el proyecto WWW, incluida una descripción del hipertexto, detalles técnicos sobre cómo crear un servidor web y un espacio para vínculos a otros servidores web a medida que entraran en línea.
Tim Berners-Lee redactó la primera propuesta para la World Wide Web en marzo de 1989 y su segunda propuesta en mayo de 1990. Su objetivo era fusionar las tecnologías en evolución de las computadoras, las redes de datos y el hipertexto en un sistema de información global poderoso y fácil de usar.
Fue a fines de 1990 que el británico demostró el desarrollo de sus ideas mostrando el primer navegador y servidor web operativo que se ejecutaba en un ordenador NeXT.
from Linux Adictos https://ift.tt/B0YLcO1
via IFTTT
Flash bulletin alert includes mitigation strategies for defending against the ransomware.
from Dark Reading https://ift.tt/H01zcRL
via IFTTT

By BY RYAN MAC AND MIKE ISAAC
The tech billionaire, who has been on the board of the company formerly known as Facebook since 2005, is backing numerous politicians in the midterm elections.
Published: February 7, 2022 at 03:09PM
from NYT Technology https://ift.tt/aImo8Xb
via IFTTT
SecurityScorecard adds digital forensics and incident response to strengthen its products.
from Dark Reading https://ift.tt/2B6ZxKg
via IFTTT
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) said today it will be transitioning away from requiring biometric data from taxpayers who wish to access their records at the agency’s website. The reversal comes as privacy experts and lawmakers have been pushing the IRS and other federal agencies to find less intrusive methods for validating one’s identity with the U.S. government online.
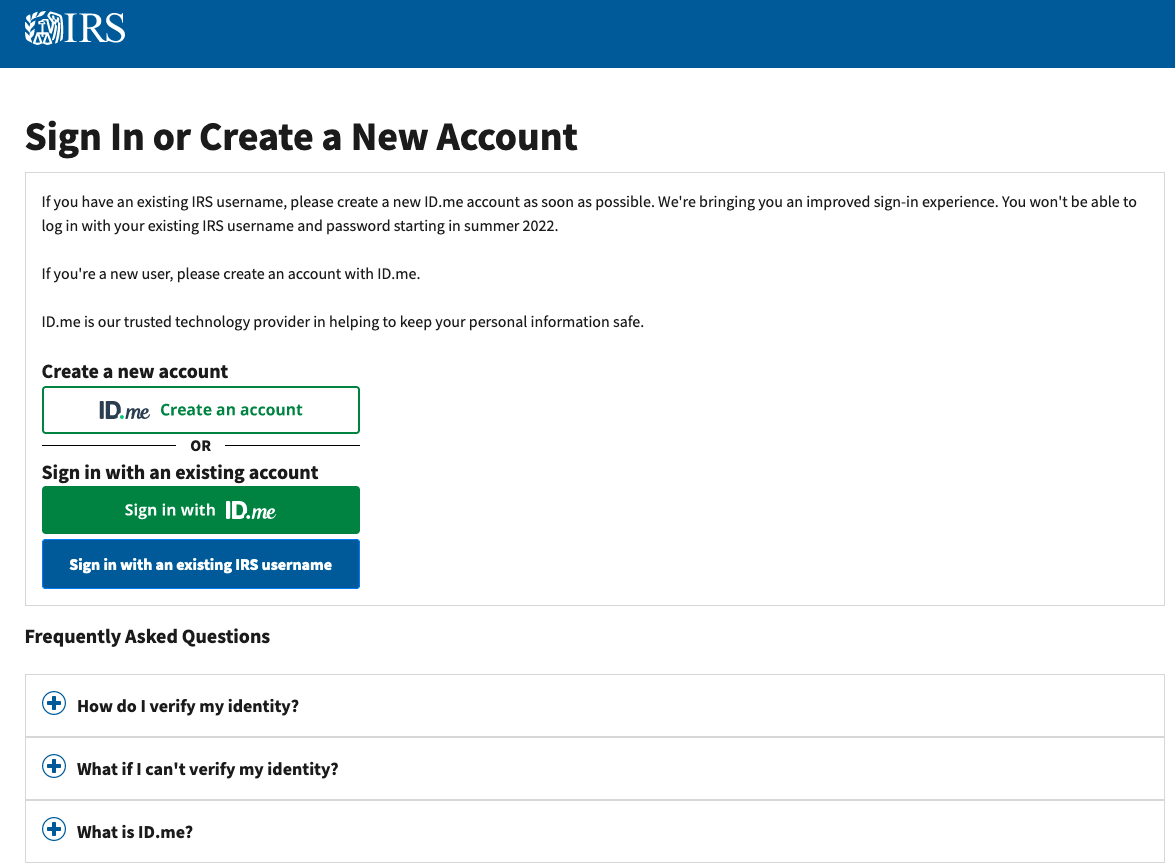
Late last year, the login page for the IRS was updated with text advising that by the summer of 2022, the only way for taxpayers to access their records at irs.gov will be through ID.me, an online identity verification service that collects biometric data — such as live facial scans using a mobile device or webcam.
The IRS first announced its partnership with ID.me in November, but the press release received virtually no attention. On Jan. 19, KrebsOnSecurity published the story IRS Will Soon Require Selfies for Online Access, detailing a rocky experience signing up for IRS access via ID.me. That story immediately went viral, bringing this site an almost unprecedented amount of traffic. A tweet about it quickly garnered more than two million impressions.
It was clear most readers had no idea these new and more invasive requirements were being put in place at the IRS and other federal agencies (the Social Security Administration also is steering new signups to ID.me).
ID.me says it has approximately 64 million users, with 145,000 new users signing up each day. Still, the bulk of those users are people who have been forced to sign up with ID.me as a condition of receiving state or federal financial assistance, such as unemployment insurance, child tax credit payments, and pandemic assistance funds.
In the face of COVID, dozens of states collectively lost tens of billions of dollars at the hands of identity thieves impersonating out-of-work Americans seeking unemployment insurance. Some 30 states and 10 federal agencies now use ID.me to screen for ID thieves applying for benefits in someone else’s name.
But ID.me has been problematic for many legitimate applicants who saw benefits denied or delayed because they couldn’t complete ID.me’s verification process. Critics charged the IRS’s plan would unfairly disadvantage people with disabilities or limited access to technology or Internet, and that facial recognition systems tend to be less accurate for people with darker skin.
Many readers were aghast that the IRS would ask people to hand over their biometric and personal data to a private company that begin in 2010 as a way to help veterans, teachers and other public servants qualify for retail discounts. These readers had reasonable questions: Who has (or will have) access to this data? Why should it be stored indefinitely (post-verification)? What happens if ID.me gets breached?
The Washington Post reported today that in a meeting with lawmakers, IRS officials said they were considering another identity verification option that wouldn’t use facial recognition. At the same time, Senate Finance Committee Chairman Ron Wyden (D-Ore.) challenged the Treasury Department and IRS to reconsider the biometric requirements.
In a statement published today, the IRS said it was transitioning away from using a third-party service for facial recognition to help authenticate people creating new online accounts.
“The transition will occur over the coming weeks in order to prevent larger disruptions to taxpayers during filing season,” the IRS said. “During the transition, the IRS will quickly develop and bring online an additional authentication process that does not involve facial recognition. The IRS will also continue to work with its cross-government partners to develop authentication methods that protect taxpayer data and ensure broad access to online tools.”
“The IRS takes taxpayer privacy and security seriously, and we understand the concerns that have been raised,” IRS Commissioner Chuck Rettig wrote. “Everyone should feel comfortable with how their personal information is secured, and we are quickly pursuing short-term options that do not involve facial recognition.”
The statement further stressed that the transition announced today does not interfere with the taxpayer’s ability to file their return or pay taxes owed. “During this period, the IRS will continue to accept tax filings, and it has no other impact on the current tax season,” the IRS said. “People should continue to file their taxes as they normally would.”
It remains unclear what other service or method the IRS will use going forward to validate the identities of new account signups. Wyden and others have urged the IRS to use Login.gov, a single sign-on service that Congress required federal agencies to use in 2015.
“Login.gov is already used to access 200 websites run by 28 Federal agencies and over 40 million Americans have accounts,” Wyden wrote in a letter to the IRS today. “Unfortunately, login.gov has not yet reached its full potential, in part because many agencies have flouted the Congressional mandate that they use it, and because successive Administrations have failed to prioritize digital identity. The cost of this inaction has been billions of dollars in fraud, which has in turn fueled a black market for stolen personal data, and enabled companies like ID.me to commercialize what should be a core government service.”
Login.gov is run by the U.S. General Services Administration, which told The Post that it was “committed to not deploying facial recognition…or any other emerging technology for use with government benefits and services until a rigorous review has given us confidence that we can do so equitably and without causing harm to vulnerable populations.”
from Krebs on Security https://ift.tt/gdKP13G
via IFTTT
Take a proactive approach to client-side security: Why monitoring your JavaScript programming language is so important to your overall security posture.
from Dark Reading https://ift.tt/K02HBbf
via IFTTT
Now that attackers can bypass preventative controls, we need to find and stop the attackers when they’re already inside.
from Dark Reading https://ift.tt/3cXW85O
via IFTTT
It’s a big deal when a vendor decides to block one of its own “features” for security reasons. Here’s why we think it’s a good idea.
from Naked Security https://ift.tt/JsoaZPq
via IFTTT