Such a program will require effort and reprioritization, but it will let your company fight modern-day threats and protect your most important assets.
from Dark Reading: https://ift.tt/2MsjTQ4
via IFTTT

Such a program will require effort and reprioritization, but it will let your company fight modern-day threats and protect your most important assets.
from Dark Reading: https://ift.tt/2MsjTQ4
via IFTTT
Federal prosecutors this week charged a Seattle woman with stealing data from more than 100 million credit applications made with Capital One Financial Corp. Incredibly, much of this breached played out publicly over several months on social media and other open online platforms. What follows is a closer look at the accused, and what this incident may mean for consumers and businesses.

Paige “erratic” Thompson, in an undated photo posted to her Slack channel.
On July 29, FBI agents arrested Paige A. Thompson on suspicion of downloading nearly 30 GB of Capital One credit application data from a rented cloud data server. Capital One said the incident affected approximately 100 million people in the United States and six million in Canada.
That data included approximately 140,000 Social Security numbers and approximately 80,000 bank account numbers on U.S. consumers, and roughly 1 million Social Insurance Numbers (SINs) for Canadian credit card customers.
“Importantly, no credit card account numbers or log-in credentials were compromised and over 99 percent of Social Security numbers were not compromised,” Capital One said in a statement posted to its site.
“The largest category of information accessed was information on consumers and small businesses as of the time they applied for one of our credit card products from 2005 through early 2019,” the statement continues. “This information included personal information Capital One routinely collects at the time it receives credit card applications, including names, addresses, zip codes/postal codes, phone numbers, email addresses, dates of birth, and self-reported income.”
The FBI says Capital One learned about the theft from a tip sent via email on July 17, which alerted the company that some of its leaked data was being stored out in the open on the software development platform Github. That Github account was for a user named “Netcrave,” which includes the resume and name of one Paige A. Thompson.
The complaint doesn’t explicitly name the cloud hosting provider from which the Capital One credit data was taken, but it does say the accused’s resume states that she worked as a systems engineer at the provider between 2015 and 2016. That resume, available on Gitlab here, reveals Thompson’s most recent employer was Amazon Inc.
Further investigation revealed that Thompson used the nickname “erratic” on Twitter, where she spoke openly over several months about finding huge stores of data intended to be secured on various Amazon instances.
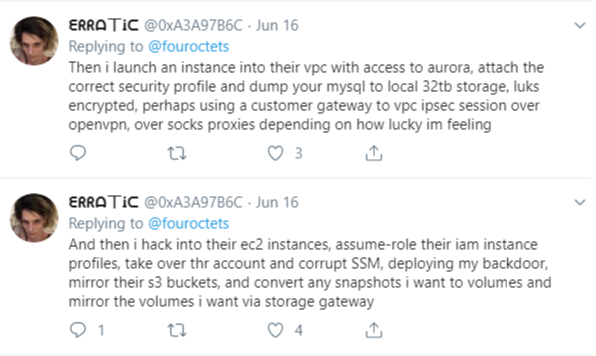
The Twitter user “erratic” posting about tools and processes used to access various Amazon cloud instances.
According to the FBI, Thompson also used a public Meetup group under the same alias, where she invited others to join a Slack channel named “Netcrave Communications.”
KrebsOnSecurity was able to join this open Slack channel Monday evening and review many months of postings apparently made by Erratic about her personal life, interests and online explorations. One of the more interesting posts by Erratic on the Slack channel is a June 27 comment listing various databases she found by hacking into improperly secured Amazon cloud instances.
That posting suggests Erratic may also have located tens of gigabytes of data belonging to other major corporations:
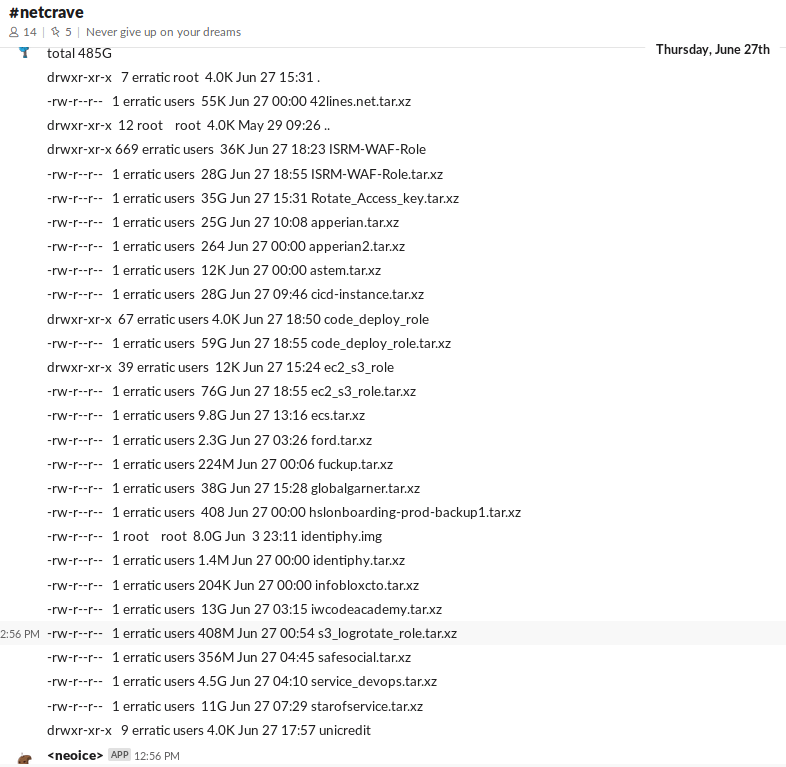
According to Erratic’s posts on Slack, the two items in the list above beginning with “ISRM-WAF” belong to Capital One.
Erratic also posted frequently to Slack about her struggles with gender identity, lack of employment, and persistent suicidal thoughts. In several conversations, Erratic makes references to running a botnet of sorts, although it is unclear how serious those claims were. Specifically, Erratic mentions one botnet involved in cryptojacking, which uses snippets of code installed on Web sites — often surreptitiously — designed to mine cryptocurrencies.
None of Erratic’s postings suggest Thompson sought to profit from selling the data taken from various Amazon cloud instances she was able to access. But it seems likely that at least some of that data could have been obtained by others who may have followed her activities on different social media platforms.
Ray Watson, a cybersecurity researcher at cloud security firm Masergy, said the Capital One incident contains the hallmarks of many other modern data data breaches.
“The attacker was a former employee of the web hosting company involved, which is what is often referred to as insider threats,” Watson said. “She allegedly used web application firewall credentials to obtain privilege escalation. Also the use of Tor and an offshore VPN for obfuscation are commonly seen in similar data breaches.”
“The good news, however, is that Capital One Incidence Response was able to move quickly once they were informed of a possible breach via their Responsible Disclosure program, which is something a lot of other companies struggle with,” he continued.
In Capital One’s statement about the breach, company chairman and CEO Richard D. Fairbank said the financial institution fixed the configuration vulnerability that led to the data theft and promptly began working with federal law enforcement.
“Based on our analysis to date, we believe it is unlikely that the information was used for fraud or disseminated by this individual,” Fairbank said. “While I am grateful that the perpetrator has been caught, I am deeply sorry for what has happened. I sincerely apologize for the understandable worry this incident must be causing those affected and I am committed to making it right.”
Capital One says it will notify affected individuals via a variety of channels, and make free credit monitoring and identity protection available to everyone affected.
Bloomberg reports that in court on Monday, Thompson broke down and laid her head on the defense table during the hearing. She is charged with a single count of computer fraud and faces a maximum penalty of five years in prison and a $250,000 fine. Thompson will be held in custody until her bail hearing, which is set for August 1.
from Krebs on Security https://ift.tt/2YgRy6D
via IFTTT
Que la batería de un móvil se “hinche” es un fallo más común de lo que piensas. Sobre todo, si el componente en cuestión no es el original, sino que ha sido reemplazado por uno no oficial, que por tanto no ha atravesado los controles de calidad del fabricante del dispositivo. Y por supuesto, intentar solucionar este problema por tu cuenta en casa y sin la supervisión de un profesional,
Entra en Andro4all para leer el artículo completo
Puedes unirte a nosotros en Twitter, Facebook o en Google+
¡Suscríbete a nuestro canal de YouTube!
Publicado recientemente en Andro4all
from Andro4all https://ift.tt/2LP0Foa
via IFTTT
Xiaomi tiene una buena serie de productos en su catálogo que no son smartphones, de hecho, la gran mayoría del mismo son otro tipo de productos que poco o nada tienen que ver con los smartphones. Y es algo a lo que, pese a que pueda parecer lo contrario, ya nos hemos llegado a acostumbrar. Sin embargo, hay ocasiones en las que todavía nos sorprendemos viendo los productos que la
Entra en Andro4all para leer el artículo completo
Puedes unirte a nosotros en Twitter, Facebook o en Google+
¡Suscríbete a nuestro canal de YouTube!
Publicado recientemente en Andro4all
from Andro4all https://ift.tt/2Mv7afL
via IFTTT
As politicians should know by now, secure messaging apps such as Telegram can quickly become a double-edged sword.
from Naked Security https://ift.tt/2ZmbFMY
via IFTTT
Apple Watch and HomePod have the highest rate of inadvertent recordings, a whistleblower says.
from Naked Security https://ift.tt/2SQugOS
via IFTTT
Two years ago, the US government fined an international cybercriminal and his fraudulent bitcoin exchange over $100m. Now, it’s going after them for the money.
from Naked Security https://ift.tt/2LOAIoU
via IFTTT

Con un poco de suspense, KDE Community ha lanzado hoy Plasma 5.16.4. El pequeño suspense ha venido porque, a diferencia de otras ocasiones, la comunidad KDE ha anunciado el lanzamiento de la última versión de su entorno gráfico antes de que estuviera disponible para su descarga, ni siquiera el código fuente. Durante varios minutos, hemos podido ver un texto “No Available Yet” que ya ha desaparecido, lo que significa que su lanzamiento ya es oficial y ya está disponible.
Plasma 5.16.4 es la cuarta versión de mantenimiento de la serie 5.16. Ha llegado para introducir 18 cambios que tenéis disponibles aquí, entre los que ellos destacan una corrección de la compilación con Qt 5.13, que ahora es posible cerrar la previsualización en LNF KCM o mejoras en el modo avión. A continuación tenéis una lista de novedades que han ido avanzando publicando en sus respectivos blogs y que ya están disponibles en la v5.16.4 de Plasma.
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
La próxima versión ya será la última actualización de mantenimiento de esta serie, un Plasma 5.16.5 que será lanzado el 3 de septiembre. La versión lanzada hoy aparecerá en las próximas horas en Discover, siempre y cuando hayamos añadido el repositorio Backports de KDE Community.
from Linux Adictos https://ift.tt/2LOA4I0
via IFTTT
Equifax is fined $675 million, while New York data breach notification law now covers biometrics, passwords, and more.
from Naked Security https://ift.tt/2YBtDhk
via IFTTT
macOS / iOS JavaScriptCore – JSValue Use-After-Free in ValueProfiles
from Exploit-DB.com RSS Feed https://ift.tt/312DNoW
via IFTTT