Researchers this month uncovered a two-year-old Linux-based remote access trojan dubbed AVrecon that enslaves Internet routers into botnet that bilks online advertisers and performs password-spraying attacks. Now new findings reveal that AVrecon is the malware engine behind a 12-year-old service called SocksEscort, which rents hacked residential and small business devices to cybercriminals looking to hide their true location online.
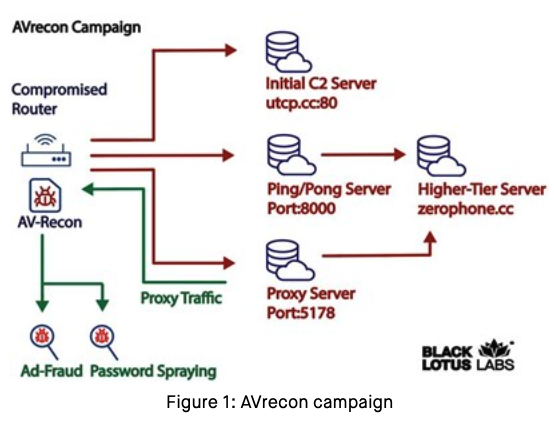
Image: Lumen’s Black Lotus Labs.
In a report released July 12, researchers at Lumen’s Black Lotus Labs called the AVrecon botnet “one of the largest botnets targeting small-office/home-office (SOHO) routers seen in recent history,” and a crime machine that has largely evaded public attention since first being spotted in mid-2021.
“The malware has been used to create residential proxy services to shroud malicious activity such as password spraying, web-traffic proxying and ad fraud,” the Lumen researchers wrote.
Malware-based anonymity networks are a major source of unwanted and malicious web traffic directed at online retailers, Internet service providers (ISPs), social networks, email providers and financial institutions. And a great many of these “proxy” networks are marketed primarily to cybercriminals seeking to anonymize their traffic by routing it through an infected PC, router or mobile device.
Proxy services can be used in a legitimate manner for several business purposes — such as price comparisons or sales intelligence — but they are massively abused for hiding cybercrime activity because they make it difficult to trace malicious traffic to its original source. Proxy services also let users appear to be getting online from nearly anywhere in the world, which is useful if you’re a cybercriminal who is trying to impersonate someone from a specific place.
Spur.us, a startup that tracks proxy services, told KrebsOnSecurity that the Internet addresses Lumen tagged as the AVrecon botnet’s “Command and Control” (C2) servers all tie back to a long-running proxy service called SocksEscort.
SocksEscort[.]com, is what’s known as a “SOCKS Proxy” service. The SOCKS (or SOCKS5) protocol allows Internet users to channel their Web traffic through a proxy server, which then passes the information on to the intended destination. From a website’s perspective, the traffic of the proxy network customer appears to originate from a rented/malware-infected PC tied to a residential ISP customer, not from the proxy service customer.
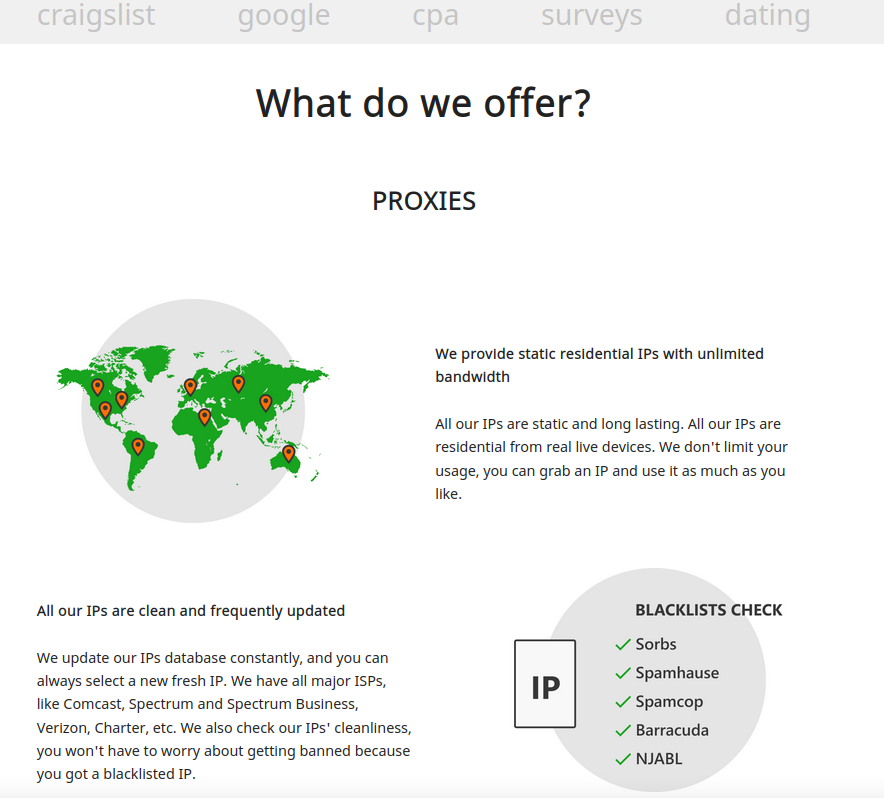
The SocksEscort home page says its services are perfect for people involved in automated online activity that often results in IP addresses getting blocked or banned, such as Craigslist and dating scams, search engine results manipulation, and online surveys.
Spur tracks SocksEscort as a malware-based proxy offering, which means the machines doing the proxying of traffic for SocksEscort customers have been infected with malicious software that turns them into a traffic relay. Usually, these users have no idea their systems are compromised.
Spur says the SocksEscort proxy service requires customers to install a Windows based application in order to access a pool of more than 10,000 hacked devices worldwide.
“We created a fingerprint to identify the call-back infrastructure for SocksEscort proxies,” Spur co-founder Riley Kilmer said. “Looking at network telemetry, we were able to confirm that we saw victims talking back to it on various ports.”
According to Kilmer, AVrecon is the malware that gives SocksEscort its proxies.
“When Lumen released their report and IOCs [indicators of compromise], we queried our system for which proxy service call-back infrastructure overlapped with their IOCs,” Kilmer continued. “The second stage C2s they identified were the same as the IPs we labeled for SocksEscort.”
Lumen’s research team said the purpose of AVrecon appears to be stealing bandwidth – without impacting end-users – in order to create a residential proxy service to help launder malicious activity and avoid attracting the same level of attention from Tor-hidden services or commercially available VPN services.
“This class of cybercrime activity threat may evade detection because it is less likely than a crypto-miner to be noticed by the owner, and it is unlikely to warrant the volume of abuse complaints that internet-wide brute-forcing and DDoS-based botnets typically draw,” Lumen’s Black Lotus researchers wrote.
Preserving bandwidth for both customers and victims was a primary concern for SocksEscort in July 2022, when 911S5 — at the time the world’s largest known malware proxy network — got hacked and imploded just days after being exposed in a story here. Kilmer said after 911’s demise, SocksEscort closed its registration for several months to prevent an influx of new users from swamping the service.
Danny Adamitis, principal information security researcher at Lumen and co-author of the report on AVrecon, confirmed Kilmer’s findings, saying the C2 data matched up with what Spur was seeing for SocksEscort dating back to September 2022.
Adamitis said that on July 13 — the day after Lumen published research on AVrecon and started blocking any traffic to the malware’s control servers — the people responsible for maintaining the botnet reacted quickly to transition infected systems over to a new command and control infrastructure.
“They were clearly reacting and trying to maintain control over components of the botnet,” Adamitis said. “Probably, they wanted to keep that revenue stream going.”
Frustratingly, Lumen was not able to determine how the SOHO devices were being infected with AVrecon. Some possible avenues of infection include exploiting weak or default administrative credentials on routers, and outdated, insecure firmware that has known, exploitable security vulnerabilities.
WHO’S BEHIND SOCKSESCORT?
KrebsOnSecurity briefly visited SocksEscort last year and promised a follow-up on the history and possible identity of its proprietors. A review of the earliest posts about this service on Russian cybercrime forums suggests the 12-year-old malware proxy network is tied to a Moldovan company that also offers VPN software on the Apple Store and elsewhere.
SocksEscort began in 2009 as “super-socks[.]com,” a Russian-language service that sold access to thousands of compromised PCs that could be used to proxy traffic. Someone who picked the nicknames “SSC” and “super-socks” and email address “michvatt@gmail.com” registered on multiple cybercrime forums and began promoting the proxy service.
According to DomainTools.com, the apparently related email address “michdomain@gmail.com” was used to register SocksEscort[.]com, super-socks[.]com, and a few other proxy-related domains, including ip-score[.]com, segate[.]org seproxysoft[.]com, and vipssc[.]us. Cached versions of both super-socks[.]com and vipssc[.]us show these sites sold the same proxy service, and both displayed the letters “SSC” prominently at the top of their homepages.
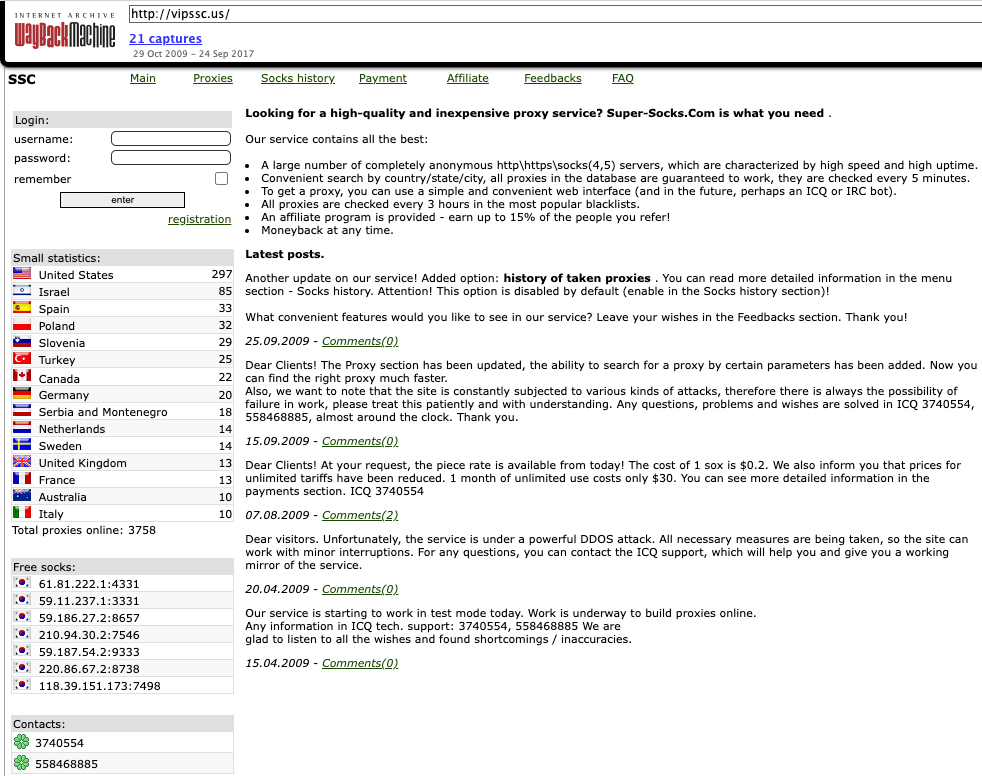
Image: Archive.org. Page translation from Russian via Google Translate.
According to cyber intelligence firm Intel 471, the very first “SSC” identity registered on the cybercrime forums happened in 2009 at the Russian language hacker community Antichat, where SSC registered using the email address adriman@gmail.com. SSC asked fellow forum members for help in testing the security of a website they claimed was theirs: myiptest[.]com, which promised to tell visitors whether their proxy address was included on any security or anti-spam block lists.
DomainTools says myiptest[.]com was registered in 2008 to an Adrian Crismaru from Chisinau, Moldova. Myiptest[.]com is no longer responding, but a cached copy of it from Archive.org shows that for about four years it included in its HTML source a Google Analytics code of US-2665744, which was also present on more than a dozen other websites.
Most of the sites that once bore that Google tracking code are no longer online, but nearly all of them centered around services that were similar to myiptest[.]com, such as abuseipdb[.]com, bestiptest[.]com, checkdnslbl[.]com, dnsbltools[.]com and dnsblmonitor[.]com.
Each of these services were designed to help visitors quickly determine whether the Internet address they were visiting the site from was listed by any security firms as spammy, malicious or phishous. In other words, these services were designed so that proxy service users could easily tell if their rented Internet address was still safe to use for online fraud.
Another domain with the Google Analytics code US-2665744 was sscompany[.]net. An archived copy of the site says SSC stands for “Server Support Company,” which advertised outsourced solutions for technical support and server administration. The company was located in Chisinau, Moldova and owned by Adrian Crismaru.
Leaked copies of the hacked Antichat forum indicate the SSC identity tied to adriman@gmail.com registered on the forum using the IP address 71.229.207.214. That same IP was used to register the nickname “Deem3n®,” a prolific poster on Antichat between 2005 and 2009 who served as a moderator on the forum.
There was a Deem3n® user on the webmaster forum Searchengines.guru whose signature in their posts says they run a popular community catering to programmers in Moldova called sysadmin[.]md, and that they were a systems administrator for sscompany[.]net.
That same Google Analytics code is also now present on the homepages of wiremo[.]co and a VPN provider called HideIPVPN[.]com.
Wiremo sells software and services to help website owners better manage their customer reviews. Wiremo’s Contact Us page lists a “Server Management LLC” in Wilmington, DE as the parent company. Records from the Delaware Secretary of State indicate Crismaru is CEO of this company.
Server Management LLC is currently listed in Apple’s App Store as the owner of a “free” VPN app called HideIPVPN. The contact information on Crismaru’s LinkedIn page says his company websites include myiptest[.]com, sscompany[.]net, and hideipvpn[.]com.
“The best way to secure the transmissions of your mobile device is VPN,” reads HideIPVPN’s description on the Apple Store. “Now, we provide you with an even easier way to connect to our VPN servers. We will hide your IP address, encrypt all your traffic, secure all your sensitive information (passwords, mail credit card details, etc.) form [sic] hackers on public networks.”
Mr. Crismaru did not respond to multiple requests for comment. When asked about the company’s apparent connection to SocksEscort, Wiremo responded, “We do not control this domain and no one from our team is connected to this domain.” Wiremo did not respond when presented with the findings in this report.
from Krebs on Security https://ift.tt/J076auA
via IFTTT